
Introduction
Pagan Pozzolan is a natural volcanic ash with numerous industrial and commercial uses. The high quality natural crystalline pozzolan deposit covers approximately five square miles the northern portion of Pagan Island in the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands. As a result of the 1981 eruption of Mt. Pagan, 200-800 million tons of uniformly high quality natural pozzolan blanket the lowlands surrounding the volcano in vast drifts ranging from 30ft to over 100ft.
Pagan Pozzolan Mining Operation
Pagan Island is located in the central Pacific Rim, about 200 miles north of Saipan, 325 miles north of Guam. It has an area of approximately 18.5 square miles and lies at the latitude 18º05’N and at the longitude of 145º45’E. The island has a natural, protected, sandy bottom deep-water harbor on the west coast that can be used for bow and stern anchoring for large vessels up to 70,000 tons.
The ABCs of Pagan Pozzolan
Advantages, Benefits, and Cost savings in the manufacturing of Portland Cement:
- Uniformity
Random Testing from various locations of the 200 million ton deposit has found that the chemical analysis and physical properties to be of the same high quality and uniformity.
- Increased production volume
In the manufacturing of cement, numerous steps are needed to complete the process. This manufacturing process requires large amounts of heavy equipment and machinery, making the capital investment for increased production capacity among the highest of all industries. By simply adding Pagan Pozzolan in the final stages of production can increase plant production capacity without the burdensome costs associated with the capital expenditures for new machinery and equipment.
- Reduced production costs
The consumption of energy is a leading factor in the production of cement and concrete. Cement manufacturing production is among the most energy intensive industrial processes, consuming approximately 5.8 million BTUs for every ton of cement produced. With the replacement of clinker with between 10%-35% of Pagan Pozzolan, the energy costs would be reduced proportionately to the amount of Pagan Pozzolan used. Thus resulting in significant cost savings.
- Reduced environmental emissions
With the large energy expenditures required in cement production, vast quantities of CO2 emissions are pumped in the fragile environment. For every ton of cement produced, approximately 1.25 tons of CO2 is released into the atmosphere due to the combustion of fossil fuels for the rotary kilns and the chemical process of calcining limestone into lime. By adding Pagan Pozzolan, the amount of greenhouse gases, namely CO2, can be substantially reduced, proportionate to the amount of Pagan Pozzolan used.
Sulfate Resistance Test
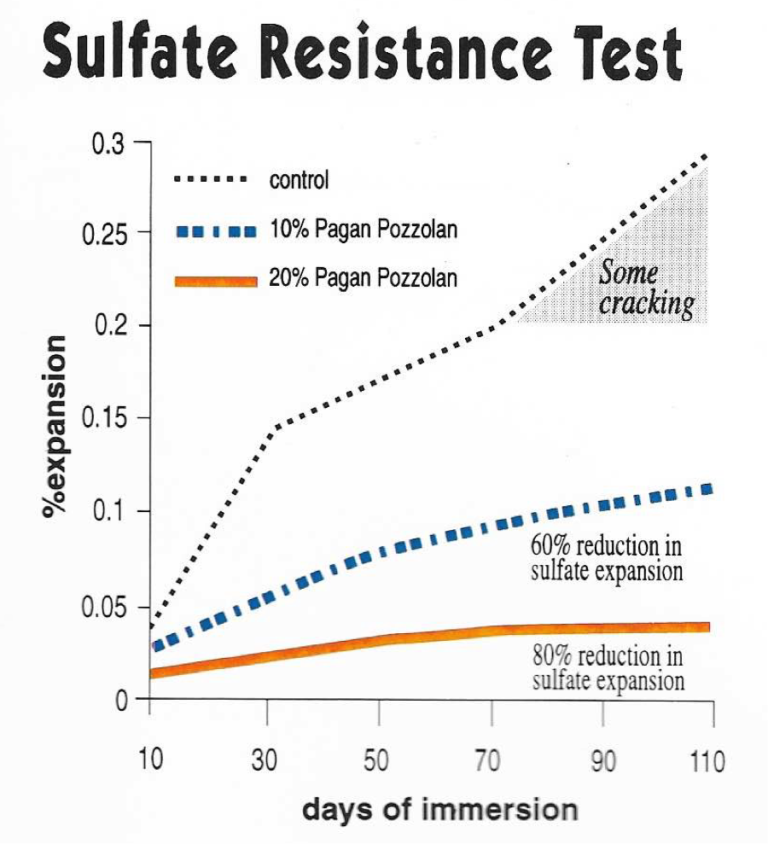
The environmental conditions in the metropolitan areas around the world, such as those in the Pacific Rim and Arabian Gulf countries can be classified as aggressive and severely corrosive. Atmospheric sulfates in these areas have reached levels that can cause erosion and micro cracking in concrete. For this reason, concrete in these regions should be designed not only for strength but also for durability. In laboratory testing (ASTM C1157), as compared to OPC, a 10% admixture of high quality Pagan Class “N” Pozzolan reduced sulfate expansion by 60%, while a 20% admixture of Pagan Pozzolan reduced expansion by 80%, eliminating micro cracking.
Alkali-Silica Reactivity
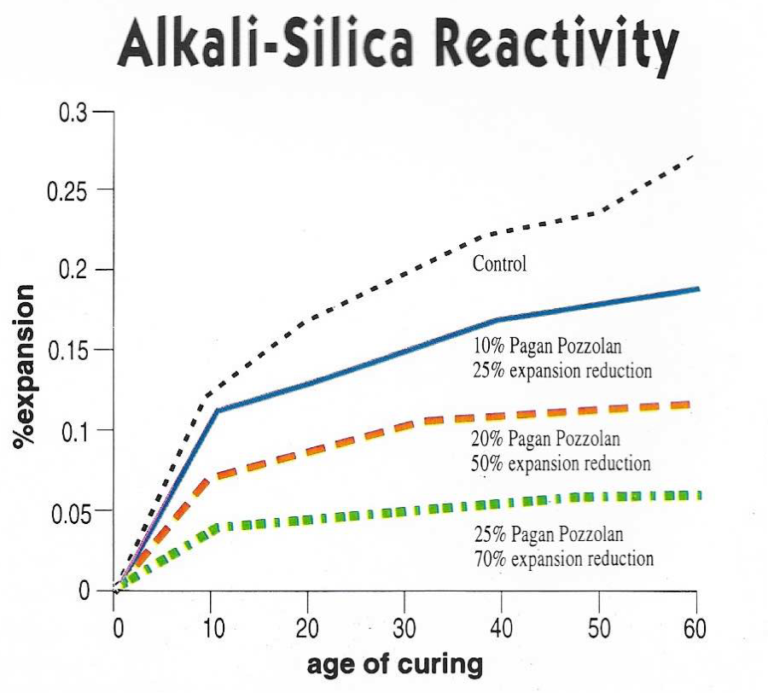
Problems associated with ASR and AAR come about due to the expansion of the concrete. In order to reduce the amount of expansion and resulting micro cracking in concrete, preventative measures must be used to assure a strong and durable concrete design. When compared with OPC, an admixture of 10% Pagan Pozzolan reduces expansion caused by alkali reactions by 25%; a 20% Pagan Pozzolan mix reduces it by 50%; and a 25% Pagan Pozzolan mix reduces alkali expansion by 70%.
Compressive Strength
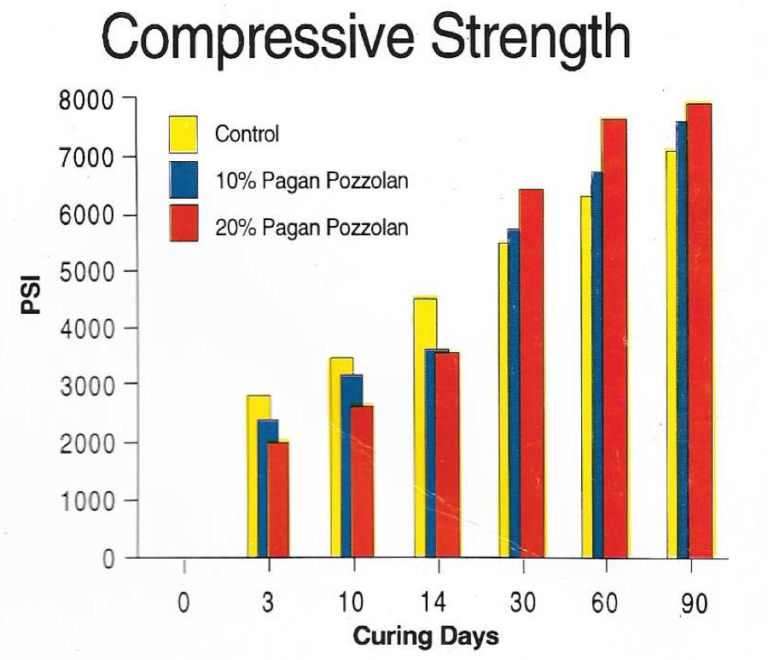
With the addition of high quality Pagan Pozzolan to cement it produces a cement mixture that not only eliminates micro cracking and permeability, but also increase overall strength and durability. Combined with the fact of a lower water requirement, low heat of hydration, ad increases in workability and pumpability, Pagan Pozzolan is a vital component to producing a superior concrete product. Pagan Pozzolan is comparable in quality with high quality Blast Furnace Slag in regards to strength and durability.
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis of Pagan Pozzolan

XRD analysis shows strong crystalline constituents, identified as mainly being plagioclases with lesser amounts of alkali feldspars. Under microscope examination, it was found that Pagan Pozzolan was quite friable and estimated to be primarily glassy with 5% being crystalline materials. The glass in pozzolan is the active material and the value of the pozzolan is dependent on its glass content, fineness and composition. The high percentage of glass in Pagan Pozzolan is a good indicator of pozzolanic potential.
Results of Natural Pagan Pozzolan Testing
Results of the natural pozzolan tested from the Pagan natural pozzolan site. The results indicate that after ball milling the material to a Blaine fineness of about 8,000 cm²/g, the material exceeds all requirements of ASTM C618 for a natural pozzolan. The sulfate resistance of the material is excellent as indicated by the low expansion values in the ASTM C1012 sulfate resistance test. Using Type II cement as the control, this material should produce the equivalent of a Type V cement.
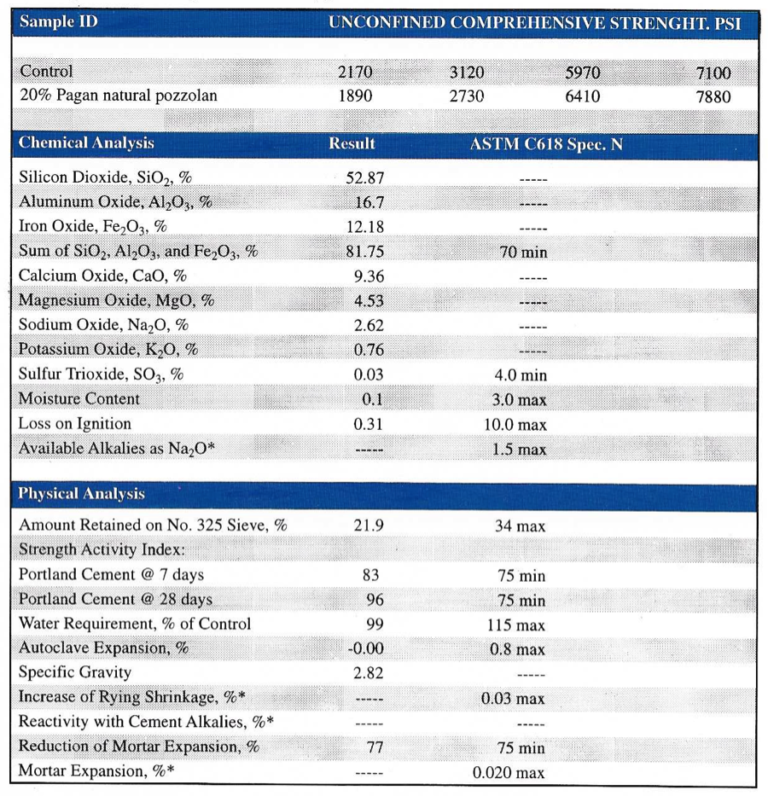
These results show that mortars containing Pagan natural pozzolan continue to gain strength versus the control at later ages, a good indicator of pozzolanic activity.
*Optional requirements. This material meets the requirements of ASTM C618 for the parameters tests. Blaine Finess= 7,810 cm²/g ; or 21,480 cm²/cm³
CTL Structural/Achitectual Engineering, Testing and Materials Technology
Pagan Pozzolan has also been tested by the CTL Structural/Achitectual Engineering, Testing and Materials Technology facility and has yielded positive results. Stated on the testing report “Based upon chemical composition and petrographic examination, Paganite (Pagan Pozzolan) is a predominantly glassy material and would be expected to exhibit good pozzolanic activity with portland cement.” It was determined that the Pagan Pozzolan is a very reactive pozzolanic material and has a very favorable potential. Details of the testing is available at the CTL Testing facility.
